Products
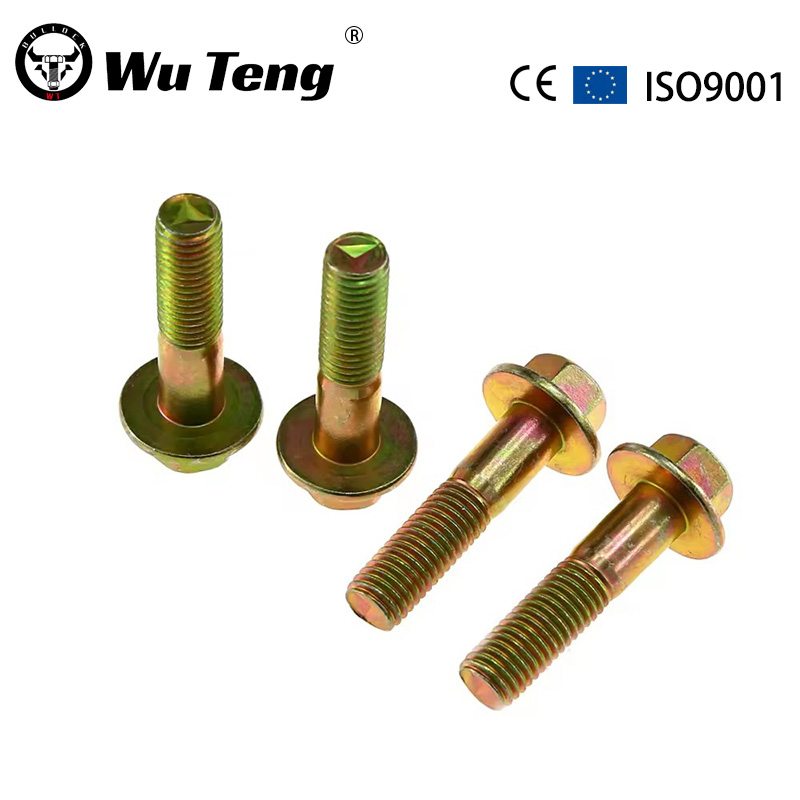
Factory Custom Yellow Zinc Plated Carbon Steel Hex Flange Head Bolt M6 M8 M10
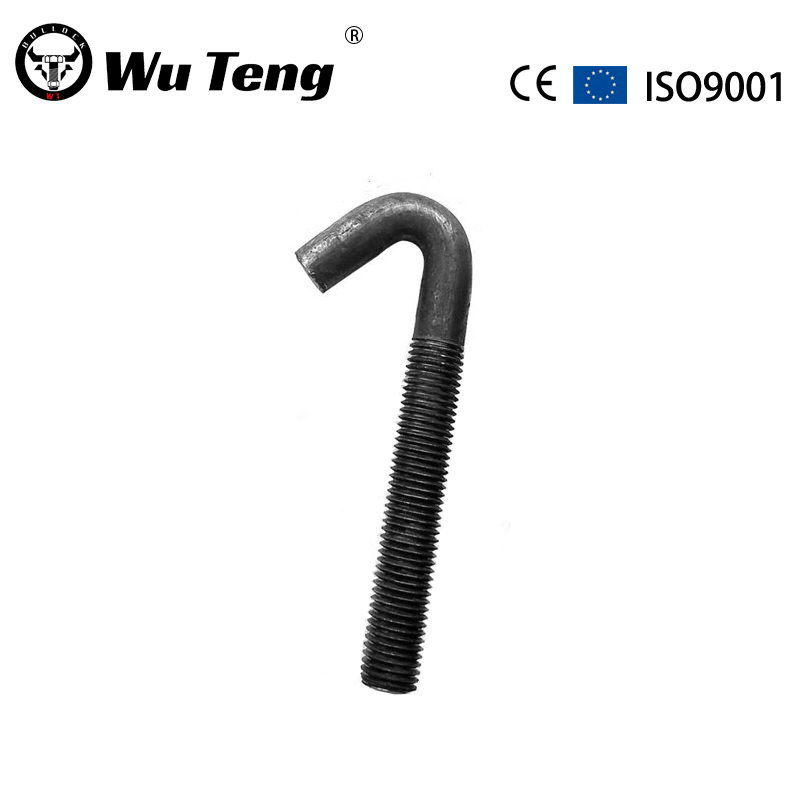
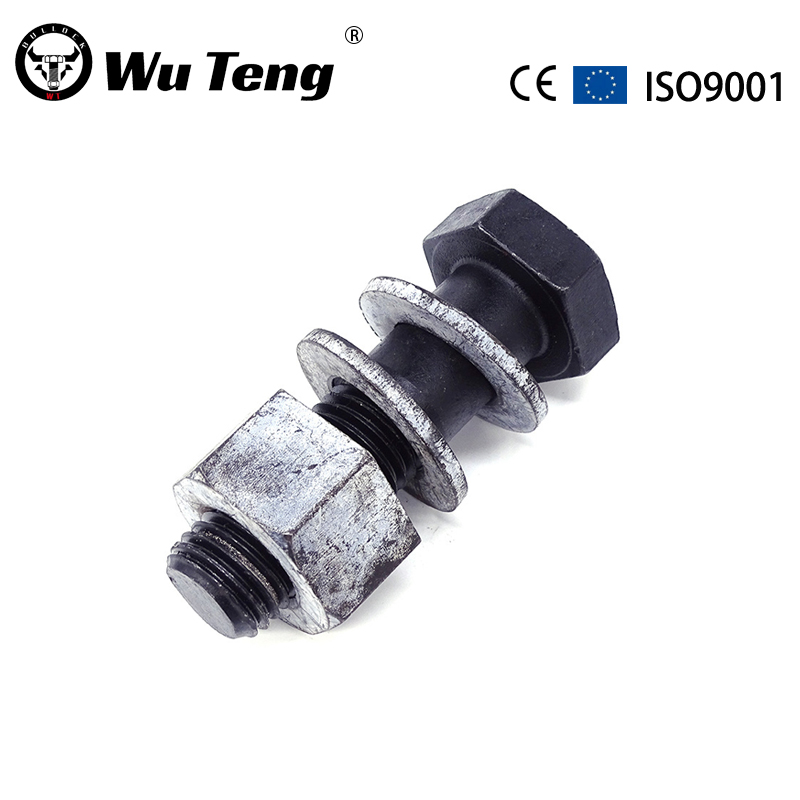
| Material | Carbon Steel, Alloy Steel, Brass, or as OEM required |
| Finish | Plain,ZincPlated(Clear/Blue/Yellow/Black), Black oxide, Nickel, Chrome, H.D.G or as required |
| Size | 1/4”–1-1/2’’; M6 – M42 or as required |
| Typical Application | Structural Steel; Metal Buliding; Oil&Gas; Tower&Pole; Wind Energy; Mechanical Machine; Automobile: Home Decorating |
| Test Equipments | Caliper,Go&No-go gauge,Tensile test machine,Hardness tester,Salt spraying tester, H.D.G thickness tester, 3D detector,Projector,Magnetic flaw detecter and etc |
| Certification | IATF 16949 , ISO 14001, ISO19001 |
| MOQ | Small order can be accepted |
| Loading Port | Ningbo , Shanghai |
| Payment term | 30% deposit in advance,70% before shipment,100% TT in advance |
| Sample | YES |
| Delivery Time | Enough stock and strong production capacity ensure timely delivery |
| Packaging | 100,200,300,500,1000PCS per bag with label,export standard carton, or according to customer special demand |
| Design ability | We can supply sample, OEM&ODM is welcome. Customized drawing with Decal,Frosted, Print are available as request |
Flange bolts are widely used in the following fields:
- Automotive manufacturing: used for connecting components such as engines and chassis.
- Mechanical equipment: assembly of various types of machine tools and industrial equipment.
- Construction engineering: plays a role in steel structure connections and other aspects.
The tightening torque of flange bolts can be determined by considering the following aspects:
- Reference bolt standards and specifications: Refer to relevant bolt standards, such as international standards (ISO), national standards (GB), etc. These standards usually provide recommended tightening torque ranges for flange bolts of different specifications and grades.
- Consider the material and strength grade of the bolt: The material (such as carbon steel, alloy steel, etc.) and strength grade (such as 8.8, 10.9, etc.) of the bolt will affect its ability to withstand torque. Generally speaking, the higher the strength level, the greater the allowable tightening torque.
- Analyze the materials and working conditions of the connecting components: The hardness and surface roughness of the connected components, as well as factors such as temperature and vibration in the working environment, can all affect the tightening torque. For example, in high temperature or high vibration environments, it may be necessary to increase the tightening torque to ensure the reliability of the connection.
- Calculate the friction coefficient: The friction coefficient between the bolt and the connected part will affect the efficiency of converting torque into preload force. By measuring or estimating the friction coefficient, the tightening torque can be calculated more accurately.
- Conduct experiments and tests: In practical applications, appropriate tightening torque can be determined through experiments. For example, using a torque wrench to gradually increase the torque while monitoring the pre tightening force of the bolts and the reliability of the connection to find the optimal tightening torque value.
It should be noted that determining the appropriate tightening torque requires comprehensive consideration of multiple factors to ensure that the flange bolt connection has sufficient pre tightening force without causing bolt damage or deformation of the connecting components due to excessive torque.
Write your message here and send it to us